From Cornfields to Capitol: Protecting the Future of Ethanol
IL Corn’s Push to Protect Farmers and Fuel Demand
From the beginning, renewable fuels have provided farmers a stronger market, helped drivers save at the pump, and moved our country toward energy independence. Corn-based ethanol gave America a homegrown solution at a time when we were highly dependent on foreign oil.
Over time, federal policy has helped grow this market. The Renewable Fuels Standard (RFS) laid the foundation by requiring cleaner, homegrown fuels like ethanol blended into the nation’s fuel supply. That policy created a reliable demand for corn, gave drivers more choices at the pump, and reduced carbon emissions.
Today, ethanol continues to be a leader in the clean fuel conversation. Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) is opening new markets, showing that corn ethanol can be a part of lowering the carbon footprint of the airline industry. The new 45Z tax credit is designed to reward low-carbon fuels starting in 2025.
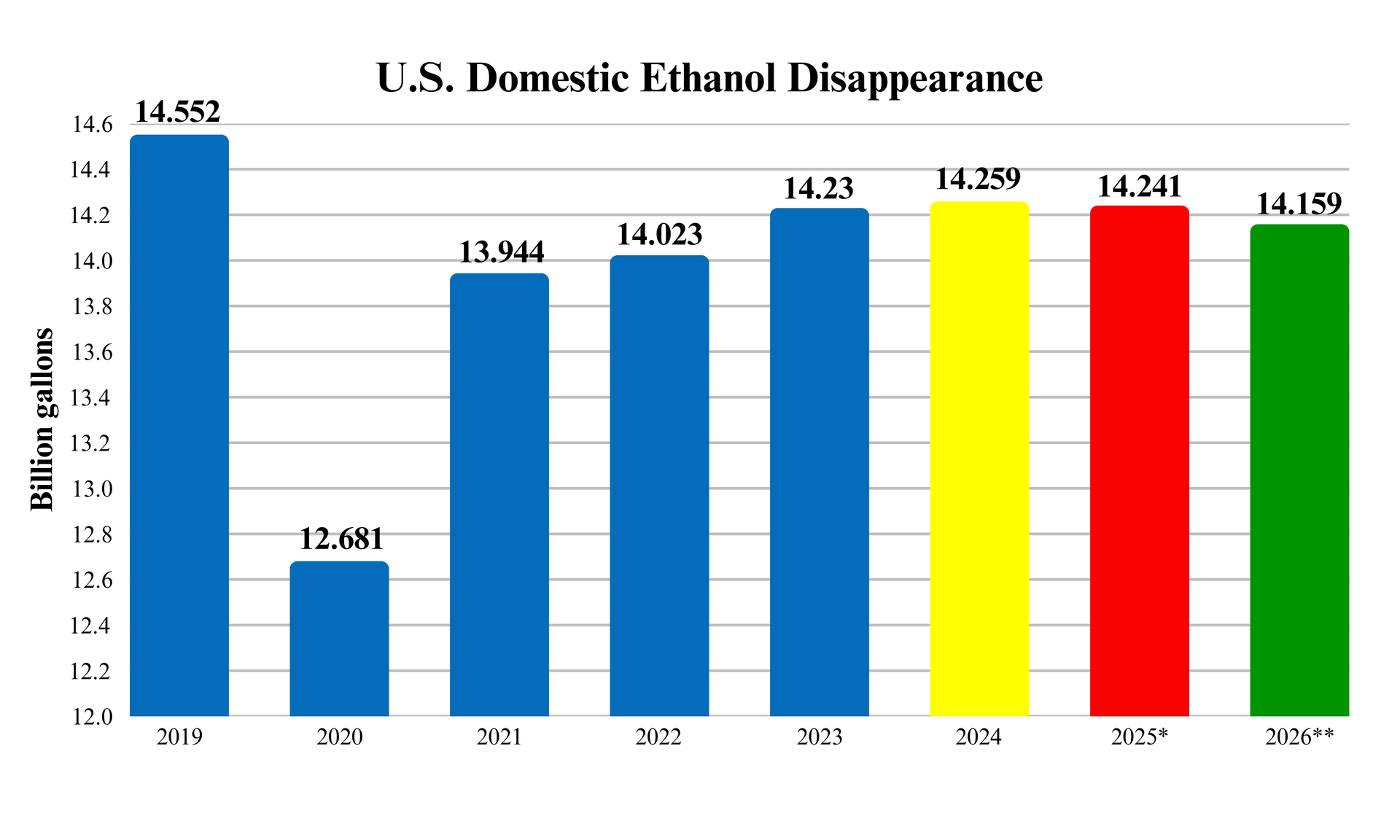
Although ethanol is the cheapest form of octane* for gasoline, we have seen a decrease in demand over the past few years.
*Octane: Measures how smoothly fuel burns in your engine. Higher octane means better performance. It’s the number you see on the yellow sticker at the gas pump.
Current legislation being introduced:
- Nationwide Consumer and Fuel Retailer Choice Act of 2025 (E15)
- Allow gasoline that is blended with 10% to 15% ethanol to be permanently sold year-round
- Current limitations prevent blends of 15% ethanol (E15) during summer months
- Emergency waivers are needed to bypass this each year
Future domestic demand for ethanol could come from high-octane legislation. By setting a higher minimum octane standard nationwide, we can empower retailers with more fuel options, provide drivers with better engine performance, and create a long-term demand for corn ethanol.
This strategy fits with President Donald Trump’s goal of strengthening America’s independence in the energy, infrastructure, and domestic production. Illinois plays a key part in reaching this goal due to our highly productive lands and history of ag production. Illinois is home to the world’s largest wet mill, ADM in Decatur, IL, and the world’s largest dry mill, Marquis in Hennepin, IL.
Ethanol has always been about building a stronger America. IL Corn is determined to advocate for legislation that grows the demand of ethanol for Illinois corn farmers.







